Legal Challenges for Startups & How to Solve Them
Date: 29/01/2025 | Corporate, Data Protection & Information Law, Regulatory Law
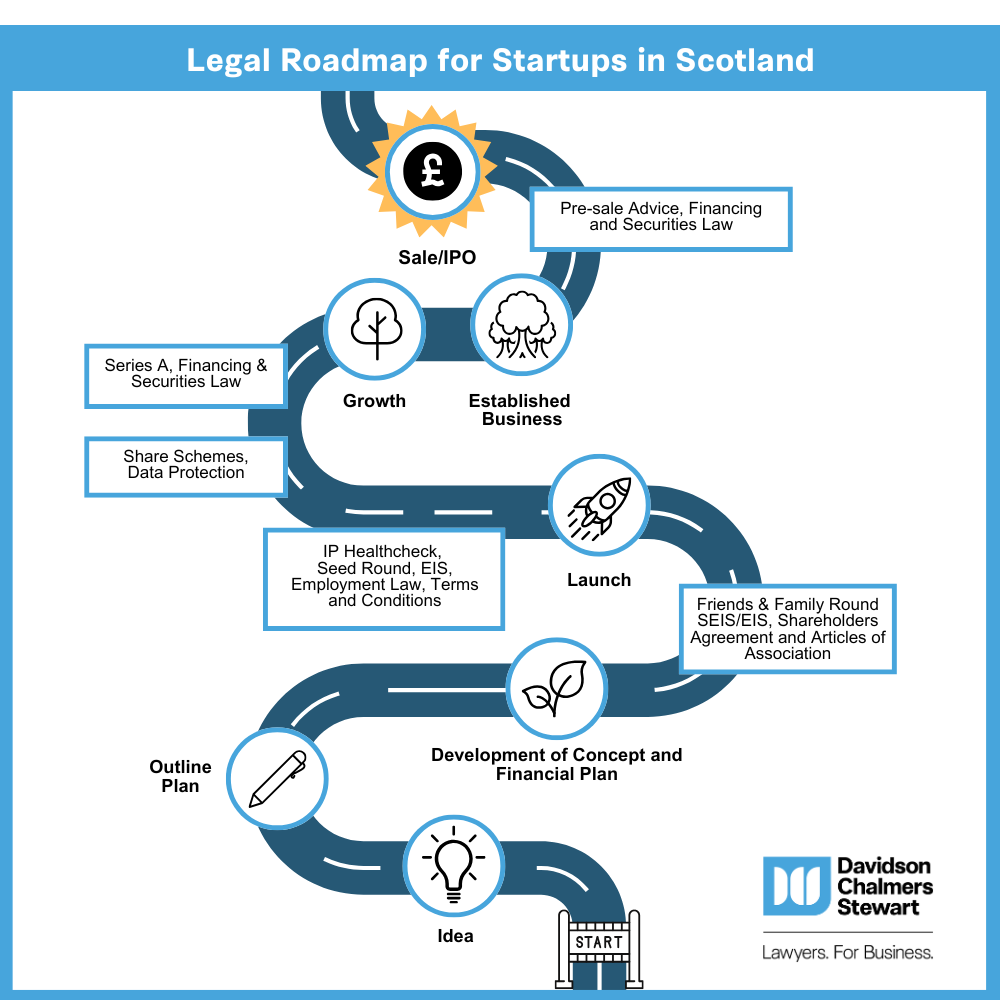
Starting a business is an exciting and complex project, full of challenges, and opportunities. As startups transition from early-stage ventures to established companies, they face a unique set of legal issues that can determine their success or failure. This article outlines some of the most critical legal challenges that startups encounter on their growth journey and provides strategies for navigating these issues effectively.
Intellectual Property Protection
For startups, intellectual property (IP) often forms the core of their value, especially if they are tech-driven or innovative businesses. Protecting IP is crucial to maintaining a competitive edge, but it presents several issues:
- Patents: Many startups rely on unique products, technologies, or processes that can be patented but, the patent application process is time-consuming, complex, and expensive. Additionally, startups may face patent infringement from competitors with deep pockets – these may be legal battles a start-up does not have the funds to fight.
- Trademarks: As startups establish their brand, protecting it through trademarks becomes essential. However, they must ensure that their brand elements don’t infringe upon existing trademarks, as this could require rebranding, which is both costly and time-consuming.
- Copyrights: For startups in creative fields, protecting original works, such as code, written content, and multimedia, through copyright is vital. Startups must understand how to manage copyright issues and ensure that third-party contractors do not retain rights over materials they produce – such as the company’s website.
- Trade Secrets: Many startups rely on proprietary information that cannot be patented or trademarked. Protecting trade secrets through confidentiality agreements and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) is crucial but can be challenging to enforce, especially in competitive industries.
Solution: Startups should prioritize IP protection early by working with experienced solicitors to establish comprehensive IP strategies. Applying for patents and trademarks and enforcing NDAs and other contractual protections are essential steps to safeguarding IP rights and making a start-up viable for outside investment.
Regulatory Compliance
As startups grow, they need to get to grips with the legal and regulatory landscape as it applies to them.
- Data Privacy: UK data protection law imposes strict rules around data collection, storage, and sharing. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to hefty fines and serious reputational damage.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Startups in certain areas for example, medical devices or financial services, face additional regulatory requirements. For example, fintech companies need to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations, while medical device companies must navigate the CE mark or FDA approval process.
- Employment Law: As startups start hiring staff they must also comply with employment laws governing things such as minimum wages, workplace safety, discrimination, and termination practices. Non-compliance with employment laws can lead to lawsuits, fine and reputational damage.
Solution: Establishing a dedicated compliance team or working with solicitors experienced in those areas can help startups comply with the laws and regulations that apply to them and keep up with changes to those regulations. Regular audits and employee training can further ensure that the company continues to operate within legal boundaries as it expands.
Financing and Securities Law
To fuel growth, startups often seek outside funding from venture capitalists, angel investors, or through sales of shares to the public. These fundraising activities come with many legal issues attached that, if mishandled, can have drastic consequences for founders and for the business.
- Issues of Shares: When issuing shares, startups must comply with all relevant securities laws. At the early stage investors will want to attract SEIS and EIS relief and structuring investment to meet the regulatory requirements is key. Failure to comply with these can lead to fines and disqualify the company from future fundraising rounds.
- Convertible Notes or ASAs: Many startups use convertible loan notes or Advance Subscription Agreements during early fundraising rounds. These instruments must be structured carefully to avoid issues with tax, future investors or regulatory bodies.
- Public Offerings: For startups that eventually go public, Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) bring a new set of challenges, including disclosure requirements, audits, and strict scrutiny from regulators.
Solution: Startups should engage experienced corporate solicitors to handle securities law compliance. Detailed planning and documentation for each funding round, coupled with investor relations management, are critical for avoiding legal pitfalls in fundraising.
Contracts and Business Agreements
Startups will require to enter into various contracts as they grow, including supplier and reseller agreements, partnership agreements, lease agreements, and more. Ensuring that these contracts are legally binding and on terms favourable to the startup’s interests is crucial.
- Supplier/Vendor Contracts: As startups scale, they depend on suppliers and resellers, making it essential to have clear and enforceable contracts. Misaligned expectations or ambiguous contract terms can disrupt operations and lead to disputes.
- Customer Contracts: Ensuring fair and compliant terms in customer contracts can be challenging, particularly when dealing with larger clients who have significant negotiation power.
- Employment Contracts: Startups also need to establish clear terms with employees, including offer letters, confidentiality agreements, and non-compete clauses where legally permissible. Clear employment contracts help protect IP and reduce legal disputes.
Solution: Consulting with contract experienced solicitors can help startups put robust agreements in place, reducing the risk of disputes. Startups should also think about putting in place standardised contract templates to streamline contract management and ensure consistency across various agreements.
Employee Relations
Employee relations become more complex as a startup grows, especially when transitioning from a small flexible team to a more structured workforce. Start-ups face several employment law challenges that can impact their growth trajectory.
- Worker Classification: Misclassifying employees as self-employed independent contractors, or vice versa, can lead to costly legal issues. There are strict penalties for misclassification, additional tax payments can arise and there can be employee relations issues.
- Proper Policies: As the workforce grows, so does the potential for workplace issues related to discrimination, harassment, and wrongful termination to name a few. It is vital that a startup puts a full set of employee policies in place quickly to protect both the start-up and the employee.
- Employee Benefits and Compensation: Startups are required to provide certain benefits, such as pension contributions and payment of minimum wage. Misunderstanding or neglecting these obligations can lead to regulatory penalties.
Solution: Startups should work with a human resources (HR) team to manage employee relations and compliance with employment laws. Creating comprehensive policies for hiring, managing, and compensating employees can help prevent employee related disputes.
Taxation and Financial Reporting
As startups grow, they encounter increasingly complex tax rules. Navigating tax laws and ensuring accurate financial reporting are crucial to avoid any legal and financial penalties.
- Corporate Tax Compliance: Startups must understand and comply with corporate tax laws, which can vary significantly depending on location and business model.
- VAT and International Taxation: Start ups must decide when they need to register for VAT and if a startup expands internationally, it must navigate the complexities of international tax laws, including sales tax and import/export duties.
- Accounting Standards and Financial Reporting: For companies seeking venture capital or planning an IPO, adhering to financial reporting standards like Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is critical.
Solution: Startups should work with experienced accountants and tax advisors who specialize in business taxation and financial compliance. Proper financial planning, audits, and periodic reviews can help prevent issues with tax authorities and ensure transparent financial reporting.
Data Security and Cybersecurity
Data security has become one of the top legal concerns for growing startups, especially those that handle sensitive customer information.
- Data Breaches and Liability: Data breaches can result in significant legal consequences, including fines and lawsuits from affected customers. Many data privacy laws mandate that companies notify customers in the event of a breach.
- Cybersecurity Regulations: Startups must comply with various cybersecurity regulations and standards, especially if they operate in sectors like finance or healthcare, where strict data protection is mandatory.
- Third-Party Data Handling: As startups often partner with third-party vendors for data management, ensuring that these vendors comply with data security standards is crucial to mitigating risks.
Solution: Startups should establish a robust cybersecurity framework, including data encryption, secure access controls, and regular security audits. Adopting industry best practices and ensuring that third-party partners adhere to the same standards can help minimize cybersecurity risks.
Conclusion
The legal challenges faced by startups as they grow are complex and multifaceted, affecting nearly every aspect of their operations. Successfully navigating these issues requires proactive legal planning, compliance with industry standards, and continuous adaptation to evolving regulatory landscapes. By addressing legal challenges early, start ups can protect their business and allow it to grow and flourish.
If you need help with the legal challenges your start up is facing as it grows, then let us know. We would be happy to help. Speak to Catherine Feechan in our Corporate Department.
This article is for general information only and nothing in it should be taken as legal advice.